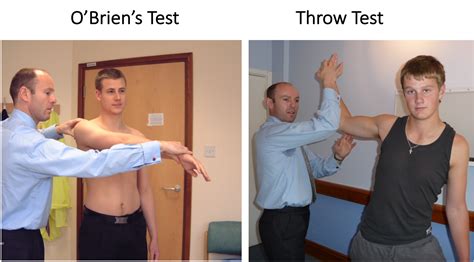
test for posterior labral tear shoulder|special tests for shoulder labrum : makers The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Resultado da Página Inicial >> SERRA DA SORTE >> Resultado do Serra da Sorte, domingo 16 de janeiro de 2022
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Publicado em 26 de janeiro de 2024 às, 16h53. Última atualização em 26 de janeiro de 2024 às, 18h15. Nos últimos dias, a revelação de um pitch deck .
Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder. Treatment may be nonoperative or operative depending on chronicity of symptoms, degree of instability, and patient activity demands.evaluate for suspected posterior labral tear, reverse Hill-Sach's lesion, or associated .Diagnosing a posterior labral tear of the shoulder can be difficult for physicians. These tears can present with a wide variety of symptoms and there are multiple physical exam tests of undetermined significance.
The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2]
A Review of the Special Tests Associated with Shoulder Examination: Part II: Laxity, Instability, and Superior Labral Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) Lesions. The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2003;31(2):301-307.Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at the back of the shoulder joint. SLAP tear : A superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear occurs at the top of the glenoid (shoulder socket) and extends from the front to the back, where the .The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). .
evaluate for suspected posterior labral tear, reverse Hill-Sach's lesion, or associated rotator cuff tearO’Brien’s Test is a special orthopaedic/orthopedic test for the shoulder that attempts to test specifically for glenohumeral joint labral tears (and more specifically for SLAP Lesions; . The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or .The active compression test: A new and effective test for diagnosing labral tears and acromioclavicular joint abnormality. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26:610-613. ↑ Owen JM, Boulter T, Walton M, Funk L, Mackenzie TA. Reinterpretation of O'Brien test in posterior labral tears of the shoulder. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2015 Jan-Mar;9(1):6-8. ↑ .
A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. .
special tests for slap tear
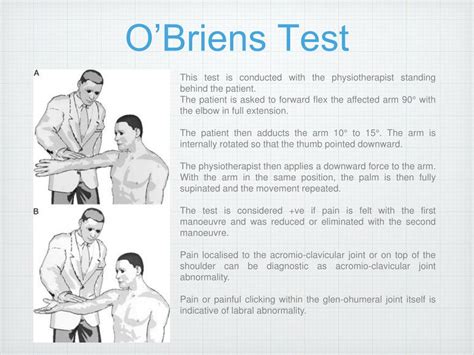
Type 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Type 3: Torn labrum tissue is caught in the .This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . Guanche CA, Jones DC. Clinical testing for tears of the glenoid labrum. Arthroscopy. 2003;19:517-523. Liu SH, Henry MH, Nuccion S, Shapiro MS, Dorey F .
laboratory blood analysis
Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum.They involve the superior glenoid labrum, where the long head of biceps tendon inserts. They may extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the labrum. Get detailed information about labral tears, including SLAP tears and Bankart tears, shoulder labral tear symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment, including surgery. . (superior labrum from anterior to posterior) tear occurs at the top of the labrum where the biceps tendon attaches. These labral tears can also damage the biceps tendon . 97% sensitive for posterior labral tear when combined with a Kim test Kim test performed by having the patient seated, arm at 90° abduction, followed by flexing the shoulder to 45 forward flexion while simultaneously applying axial load on the elbow & posterior-inferior force on the upper humerus.
Posterior labral tear. The SLAP tear can continue posteriorly and can contribute to posterior shoulder pain. In some cases the posterior labral tear can form a flap valve and a cyst will develop. This cyst can also cause posterior shoulder pain, and when it is large, it can compress the suprascapular nerve, causing weakness of shoulder rotation. Posterior shoulder dislocation: . A “clunk” sound or clicking sensation can indicate a labral tear even without instability. 12. . A reliable and simple test for posterior instability of . Sudden pain in the shoulder denotes a positive test. Kim et al. reported a 97% sensitivity for detecting posterior instability when both the jerk test and Kim test were positive. Evaluation. Plain Radiographs. . In the setting of a posterior labral tear, treatment generally consists of arthroscopic labral repair with suture anchors with or .
special tests for shoulder labrum
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK The Porcellini Test appears to be a highly valid test to assess for posterior labral tears in the shoulder.G.The accuracy of the jerk test in detecting a posteroinferior labral lesion was the following: sensitivity, 73%; specificity, 98%. The Kim test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly inferior labral lesion, whereas the jerk test was more sensitive in detecting a predominantly posterior labral lesion.
Your shoulder is where the rounded top of your upper arm bone fits into the socket of your shoulder blade ().A ring of cartilage lines and extends the socket to support the shoulder joint.. This ring of cartilage is called your glenoid labrum. When your shoulder bone is forced out of its socket and into the glenoid labrum, it can tear it or even separate it from the bone. Posterior Labral Tear Neurovascular Disorders . performed by flexing shoulder to 90°, flex elbow to 90°, and forcibly internally rotate driving the greater tuberosity farther under the CA ligament. . Posterior Stress Test. positive if there is pain and sense of instability with the maneuver. technique. Place the patient's arm in flexion .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B. SLAP stands for "superior labrum from anterior to posterior." This type of shoulder labral tear occurs at the top (“superior”) of the glenoid labrum where it connects to the biceps tendon, and it extends in a curve from the .
There are several places and ways your shoulder labral could be torn: in the front of the shoulder (anterior tear), in the back (posterior tear), and commonly both, in a tear called s uperior labrum anterior posterior, meaning the tear runs from the upper part of the labrum to the back and the front.Posterior Labral Repair Rehabilitation Protocol (Arthroscopic or Open) 0-2 weeks post-op: Goals . • Shoulder sub-maximal (pain free) isometrics with sling/immobilizer in all directions: flexion, . For throwing athletes: perform isokinetic testing below (if available). If passes test, begin interval throwing program. Re-test monthly until .
All patients were examined preoperatively for Porcellini test, and the presence of posterior labral tear was confirmed on arthroscopy. Later, in a cohort study on 91 consecutive patients who underwent shoulder arthroscopic procedures, we compared its accuracy with O'Brien's test, the Kim test, the Jerk test, and the Load and Shift test.
shoulder labral tear special tests

Posterior Labral Tear Neurovascular Disorders . generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and biceps tendonitis. . "peel back" test shows "peel back" of the labrum with 90° of external rotation and abduction.A shoulder labral tear is an injury to the ring of cartilage in the shoulder joint. Two of the most common tears are the SLAP (Superior Labral tear form Anterior to Posterior) tear and the Bankart tear. Some kinds of labral tears - especially a Bankart lesion - can increase the potential for shoulder dislocations.

After a shoulder labrum tear, you may benefit from physical therapy to help control your shoulder pain and improve your arm movement. Your physical therapist will guide you through your rehabilitation with exercises in the physical therapy clinic and will also prescribe exercises for you to do on your own at home.. Physical therapy for a shoulder labrum tear .The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous complex that attaches as a rim to the articular cartilage of the glenoid fossa. Its role is to deepen and increase the surface area of the glenoid (acting as a static stabiliser of the glenohumeral joint); resist anterior and posterior movement and assist with blocking shoulder dislocation and subluxation at the maximal ranges of motion.
Take the labrum tear test. There are 4 tests your doctor will conduct on your shoulder that specifically identify a labrum tear. If you respond in pain to any of the test, your test will be considered a pass for that specific test. Depending on how many test you pass or fail, the doctor will be able to conclude a percentage chance of a labrum tear.
posterior labrum tear: Injuries to the back of the shoulder joint can cause a posterior labrum tear. These are rare and make up only 5 to 10 percent of all shoulder injuries. Symptoms of a labral tear Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of .
laboratory biochemistry analysis
laboratory browning analysis
Segunda Via flash – Pelo Telefone. Outra maneira de realizar a emissão de uma segunda via da conta Flash é através do contato via telefone com a empresa. Para isso, siga o seguinte passo a passo: Ligue para a central de atendimento Flash no núemero: 96 3084-5051; Em seguida, informe os dados do titular da conta, como solicitado;
test for posterior labral tear shoulder|special tests for shoulder labrum